Fibromyalgia
Fibromyalgia is a complex chronic disorder characterized by widespread body pain that affects individuals physiologically, mentally and socially. Fibromyalgia is associated with pain over multiple tender points on the body including tenderness of the joints, muscles, tendons and other soft tissues. In addition the patient may experience fatigue, sleep disturbances, depression, and anxiety. In severe cases, the condition can be extremely debilitating and may interfere with daily living activities.
Causes.
The cause of fibromyalgia is not known, but certain factors such as sleep disorders, physical or emotional trauma, viral infections, and abnormal pain perception can trigger fibromyalgia.
Middle aged women are at an increased risk of developing the condition. Several other conditions such as chronic neck or back pain, chronic fatigue syndrome, Lyme disease, hypothyroidism, sleep and depressive disorders may mimic the symptoms of fibromyalgia and may coexist with it.
Symptoms.
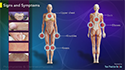
The predominant symptom of fibromyalgia is generalized body pain. The intensity of pain varies from mild to severe. Tender points, localized painful areas in the neck, shoulders, back, hips, arms or legs, are present. Any touch or firm pressure over the tender points may induce the pain sensation. The pain may either be continuous or there may be a diurnal variation in pain, with an aggravation of the pain during the night. The pain may either be aching in nature or a shooting, burning pain that may increase with stress, anxiety, physical activity and cold or damp weather. Most people with fibromyalgia also experience fatigue, depression, and sleep disorders where they wake up with a feeling of tiredness despite long periods of sleep.
People with fibromyalgia may also have other associated symptoms such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), headache, memory and concentration disorder, numbness and tingling sensation in the hands and feet, irregular heartbeat, and decreased ability to exercise.
Diagnosis.
The diagnostic criteria for fibromyalgia includes:
Widespread pain lasting for at least three months.
Pain in at least 11 of the 18 tender points including elbows, buttocks, chest, knees, shoulders, lower back, neck, rib cage, and thighs.
Blood and urine tests may be recommended to rule out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatment.
The treatment for fibromyalgia is aimed at resolution of the symptoms and helping the patient to cope with the symptoms and improve their quality of life. Treatment options for fibromyalgia include physical therapy, fitness and exercise program, and stress relief techniques such as light massage or other relaxation techniques. Swimming or exercising in a warm or heated pool may be beneficial to reduce pain, joint stiffness and relax the joints.If required medication may be prescribed to improve pain tolerance and avoid sleep disturbances. Several medications such as antidepressants, muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants (anti-seizure), and pain killers can be prescribed for initial pain management. These medications provide symptomatic relief from pain and also improve quality of sleep.
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is an important aspect of fibromyalgia treatment and helps in modification of an individual’s response to pain. Support groups may be also helpful in managing fibromyalgia. Psychotherapy or counselling also may be useful to deal with issues related to fibromyalgia. A well-balanced diet,exercise program, abstinence from caffeine, following a regular sleep pattern, performing some relaxation techniques and being educated about the condition are all helpful to live a healthy life with fibromyalgia. Other therapies such as acupuncture therapy also may be applicable to relieve the symptoms.
In severe cases the patient may require a referral to a pain clinic.
Fibromyalgia is a chronic disorder characterized by widespread pain and tenderness over the tender points of various parts of the body.