Sjogrens Syndrome
A healthy immune system helps our body to fight off infections and disease. But an overactive immune system attacks the bodies own cells and tissues causing autoimmune diseases.
Sjogren's syndrome is an auto-immune disease characterized by dry eyes and dry mouth. It often occurs as a complication of other auto-immune diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus. It can develop at any age but is more common in people older than 40 years. Women are 10 times more prone to develop the condition.
Causes.
The exact cause of the disease is not known. The presence of certain genes in an individual increases the susceptibility to the condition. Often, an infection acts as a trigger and makes the immune system over reactive causing the immune system, which normally protects the body from various infections and cancer, to now attack its own tissues. In sjogren syndrome, moisture secreting tear glands of the eyes and salivary glands of the mouth are the first body tissues that are affected. Other body parts such as joints, thyroid, kidneys, liver, lungs and skin may also become affected.
Symptoms and complications.
Decreased tears and saliva lead to the two main symptoms of Sjogren’s syndrome dry eyes and dry mouth. Dry eyes can feel gritty and itch or burn. Dry eyes may also cause light sensitivity and blurred vision. Moreover, dry eyes increase the risk of eye infections and corneal ulcers.
Dry mouth feels dry and uncomfortable making it difficult to even swallow and speak. It also increases the risk of dental decay, gingivitis (gum inflammation) and oral yeast infections (thrush).
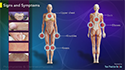
Other symptoms of sjogren’s syndrome may include:
stiffness, swelling and pain in joints.
dry skin or skin rashes.
vaginal dryness.
persistent dry cough.
prolonged weakness.
Some patients may experience episodes of painful swelling in the salivary glands, particularly in those behind the jaw and in front of the ears.
Other rare complications of Sjogren's syndrome may include adverse effects on the lungs, kidneys or liver function, numbness in hands and feet (peripheral neuropathy) and cancer of the lymph glands.
Diagnosis.
The two main early symptoms of sjogren's syndrome, dry eyes and dry mouth, can also occur from various other conditions and medications. Therefore diagnosis of sjogren’s syndrome depends on a combination of physical examination, special tests to confirm symptoms of dry eyes and dry mouth, blood tests to detect antibodies typical of an auto-immune disease, and possibly a biopsy of the salivary gland under the surface of the inner lip may also be ordered.
Diagnostic tests that may be used to diagnose Sjogren's Syndrome include the following:
Eye tests: This includes the shirmer test to confirm dryness of the eye and slit lamp test to examine the surface of the eye and cornea.
Dry mouth test: This may include a simple spit test or special imaging tests such as a sialogram ( X-ray of the salivary glands) and salivary scintigraphy ( salivary gland function test based on a radioactive isotope)
Blood tests: These mainly include tests for anti-nuclear antibodies, rheumatoid factor, anti-SSA and anti-SSB antibodies. Blood tests to determine damage to the liver or kidneys may also be ordered.
Chest X-ray: This may be ordered to detect any lung inflammation.
Urine sample may also be analyzed to determine any effect on the kidneys.
Treatment.
The type and intensity of symptoms experienced with Sjogren's syndrome varies among different patients. Treatment is aimed at relieving the symptoms as there is no cure for Sjogren’s syndrome.
Artificial tears or gels are usually recommended for dry eyes. In severe cases, a minor surgical procedure to seal the tear ducts either temporarily with collagen or silicone plugs or permanently through laser may be recommended.
Medications may be prescribed to increase production of saliva or to address specific complications such as arthritis or yeast infection in the mouth. To treat serious systemic symptoms such as fever, rashes, abdominal pain or lung or kidney problems immunosuppressive agents and/or corticosteroids may be given.
Sjogren’s syndrome is an autoimmune condition that cannot be cured but proper treatment can help in relieving symptoms.