Balloon Implant for Rotator Cuff Tears
The balloon implant for rotator cuffs is a new, innovative solution for the arthroscopic treatment of massive irreparable rotator cuff tears. It involves placement of a biodegradable implantable balloon (spacer) into the subacromial space of the shoulder arthroscopically. The purpose of the spacer is to help heal ruptured or torn rotator cuff muscles following rotator cuff repair and to decrease friction between the acromion and the humeral head or rotator cuff to enable smooth movement of the humeral head against the acromion.
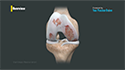
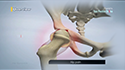
The subacromial space is the space between the acromion and the top surface of the humeral head. This space houses several soft tissue structures such as the rotator cuff, bicep tendon, and bursa, which are instrumental in the proper functioning of the shoulder.
Anatomy
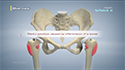
The shoulder joint is a ball and socket joint with the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) forming the ball, and the cup-shaped depression on the shoulder blade (glenoid fossa) forming the socket. The rotator cuff is a group of four tendons that join the head of the humerus to the deeper shoulder muscles to provide stability and mobility to the shoulder joint. Major injury to these tendons may result in a condition called rotator cuff tear. The tear results in symptoms such as severe pain, swelling, stiffness, weakness of the arm, and loss of joint motion.
Indications
The main indication for a balloon implant is to treat irreparable, massive rotator cuff tears caused by trauma. Your surgeon may also recommend a spacer implant in the following scenarios:
- For individuals who are not suitable candidates for standard tendon transfer treatment for rotator cuff repair
- In patients who manifest proximal humeral migration secondary to massive full-thickness rotator cuff tears
- In seniors suffering rotator cuff tendon degradation with mild to moderate glenohumeral osteoarthritis
- In patients with multiple comorbidities and who are contraindicated to undergo general anesthesia or open surgery
Preparation
Preoperative preparation for a balloon implant for rotator cuff tears may involve the following:
- A thorough history and physical examination
- Routine blood work and imaging
- Informing your doctor of any medications or supplements you are taking
- Informing your doctor of any allergies to medications, anesthesia, polymers, or latex
- Refraining from solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to surgery
- Arranging for someone to drive you home following surgery
Surgical procedure
The balloon implant procedure is similar to other standard rotator cuff operations and is commonly performed as a minimally invasive arthroscopic technique under general or regional anesthesia.
The procedure generally involves the following steps:
- After cleaning the skin over the shoulder area, your surgeon makes a few small entry points known as keyhole incisions in your shoulder joint.
- An arthroscope, a slender tubular device attached with a light and a small camera at the end, is inserted through one of the incisions into your shoulder joint.
- The camera transmits the image of the inside of your shoulder joint onto a monitor for your surgeon to view.
- Your surgeon then guides miniature surgical instruments through the other tiny incisions to perform surgical debridement of the joint area (removal of damaged tissue). Care is taken to prevent damage to healthy tissue.
- After adequate repair of the torn rotator cuff, the balloon spacer is implanted between the humeral head and the acromion and is inflated with a normal saline solution.
- The inflated spacer decreases subacromial friction and creates more space between the humeral head and coracoacromial arch.
Postoperative care
Following balloon implantation, your shoulder will be wrapped with dressings and immobilized in a sling for a few weeks to promote healing and rest the shoulder. Pain medications and antibiotics are prescribed to control pain and prevent surgery-related infection. Instructions will be given on how to remove the sling and perform gentle range-of-motion exercises soon after the surgery. Instructions on surgical site care and bathing will be provided to keep the wound clean and dry. You should avoid strenuous activities and lifting heavy weights for a defined period. You should be able to resume your normal activities in a couple of weeks, but with certain activity restrictions. An individualized physical therapy protocol is designed to help strengthen shoulder muscles and optimize shoulder function.
Benefits
Some of the advantages of a balloon implant for rotator cuff tears include:
- Improved shoulder range of motion
- Safe and low risk of complications
- Minimal postoperative pain
- Minimal damage to muscles
- Quick rehabilitation and recovery
- Cost-effective
Risks and Complications
Risks and complications of a balloon implant include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Inflammation
- Damage to surrounding soft-tissue structures
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Implant migration
Summary
The balloon implant or spacer acts as a substitute for the fluid-filled sac called a bursa that protects and cushions your shoulder joints. The bursa usually becomes inflamed and causes pain when the rotator cuff muscles rupture. The biodegradable subacromial spacer creates adequate room between the shoulder and the scapula, acromion, and humerus bone, thereby providing pain-free and friction-free shoulder motion.