Quadriceps Tendon Rupture and Repair
A quadriceps tendon rupture is defined as a tear of the quadriceps tendon as a result of a traumatic incident.
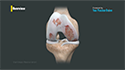
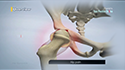
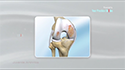
The quadriceps tendon is a strong rope-like fibrous tissue located at the top of the patella or kneecap that connects the quadriceps muscles to the kneecap. It works together with the quadriceps muscles to allow us to straighten our leg. The quadriceps muscles are the muscles located at the front of the thigh.
A quadriceps tendon rupture can be either partial or complete. A partial rupture does not completely damage the soft tissue. A complete rupture cuts the soft tissue into 2 pieces with the quadriceps muscles no longer attached to the kneecap. Small ruptures of the tendon can make walking and participation in other daily activities difficult, whereas large ruptures can be a disabling injury that normally requires surgical intervention to repair and regain complete knee function.
Causes
A quadriceps tendon rupture most commonly occurs in middle-aged people who participate in sports that involve jumping and running. The rupture can occur due to a fall, direct blow to the leg, or from landing on the leg awkwardly from a jump. Other causes include tendonitis (inflammation of quadriceps tendon) and diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, diabetes, infection, and chronic kidney failure that weakens the quadriceps tendon resulting in tears. Use of medications such as steroids and some antibiotics can also weaken the quadriceps tendon leading to ruptures.
Signs and Symptoms
Some of the common signs and symptoms of a quadriceps tendon rupture include:
- A popping sensation
- Pain and swelling
- Inability to straighten the leg
- A depression at the top of the patella
- Tenderness
- Bruising
- Cramping
- A Sagging kneecap
- Trouble walking due to buckling of the knee
Diagnosis
To identify a quadriceps tendon rupture, your doctor will review your medical history and perform a physical examination of your knee. Some imaging tests such as an X-ray or MRI scan may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis. An X-ray of the knee is taken to determine the position of the kneecap and an MRI scan is done to view the extent and location of the rupture.
Treatment
A quadriceps tendon rupture can be treated by both non-surgical and surgical methods.
Non-Surgical Treatment
Most cases of small or partial ruptures are treated with a nonsurgical approach. Non-surgical treatment involves the use of a knee brace or immobilizer to keep the injured knee straight and help it heal. Crutches may be needed to prevent the joint from bearing weight during the healing process. Physical therapy may be recommended to restore strength and increase range of motion of the knee once the initial swelling and pain have diminished.
Surgical Treatment
Most individuals with a complete rupture will need surgery to repair the tendon. However, people with a large partial rupture or a partial rupture related to tendon degeneration may also require surgery.
The surgery is most commonly performed in an inpatient setting with the patient requiring at least a one night stay in the hospital. The goal of the surgery is to re-attach the torn tendon to the kneecap and to restore the normal function of the knee.
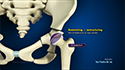
During the surgery, general or regional anesthesia is administered to the patient. An incision is made over the tendon at the knee. Sutures are placed in the torn tendon which is then passed through holes that are drilled in the kneecap. The sutures are then tied at the bottom of the kneecap to pull the torn edges of the tendon back to their normal position.
Postoperative Care
Following surgery, you will require pain management with medications and ice packs. Incision site care and bathing instructions will be provided. You should refrain from strenuous and heavy lifting activities. Staples or sutures will be removed from the incision site 2 weeks after surgery. A long cast or knee immobilizer will be applied to protect the repair. You will require the use of a brace and crutches until you are able to walk without assistance. Physical therapy exercises will be recommended to strengthen knee muscles and optimize knee function. Complete healing of the tendon will take about 4 months.
Risks and Complications
Some of the risks and complications of quadriceps tendon rupture repair include:
- Re-rupture of the tendon
- Loss of knee motion
- Muscle weakness
- Infection
- Blood clots
- Anesthetic/allergic reactions
- Wound breakdown
Summary
Quadriceps tendon rupture is an uncommon injury that usually warrants surgical treatment. Middle-aged individuals who are active in sports are more prone to having a quadriceps tendon rupture. With suitable and timely care, most individuals are able to return to their normal activities and occupations. Recovery varies from individual to individual and depends on active participation in your post-surgical rehabilitation exercises.