Shoulder Joint Replacement
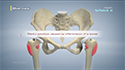
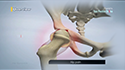
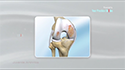
The shoulder is a highly movable body joint that allows various movements of the arm. It is a ball-and-socket joint, where the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) articulates with the socket of the scapula (shoulder blade) called the glenoid. The two articulating surfaces of the bones are covered with cartilage, which prevents friction between the moving bones. The cartilage is lubricated by synovial fluid. Tendons and ligaments around the shoulder joint provide strength and stability to the joint.
When the cartilage is damaged, the two bones rub against each other resulting in pain, swelling and stiffness of the joint (osteoarthritis).
Total shoulder replacement surgery is performed to relieve these symptoms. In this surgery, the damaged articulating parts of the shoulder joint are removed and replaced with artificial prostheses. Replacement of both the humeral head and the socket is called a total shoulder replacement.
Indications
Total shoulder joint replacement surgery is indicated for conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis when medication, injections, physical therapy, and activity changes do not help relieve the pain. Your doctor recommends surgery when you have the following symptoms:
- Severe shoulder pain that restricts daily activities
- Moderate-to-severe pain during rest
- Weakness and/or loss of motion
Diagnosis
To decide whether total shoulder replacement is a good option for you, the surgeon will evaluate your condition thoroughly.
Your surgeon reviews your medical history and performs a physical examination of your shoulder to assess the extent of mobility and pain. Imaging tests such as X-ray or MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) are ordered.
Procedure
The surgery is done under regional or general anesthesia. An incision is made over the affected shoulder and the underlying muscles are separated to expose the shoulder joint.
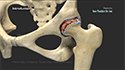
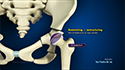
The upper arm bone (humerus) is separated from the glenoid socket of the shoulder bone. The arthritic or damaged humeral head is cut and the humerus bone is hollowed out and filled with cement. A metal ball with a stem, is gently press-fit into the humerus.
Next, the arthritic part of the socket is prepared. The plastic glenoid component is fixed into the shoulder bone.
After the artificial components are implanted, the joint capsule is stitched, and the wound is closed.
Post-operative Care
After the surgery, medications are prescribed to control any pain and your arm may be placed in a sling. The rehabilitation program includes physical therapy, which is started soon after the surgery and is very important to strengthen and provide mobility to the shoulder. You may be able to perform gentle daily activities two to six weeks after surgery.
Risks and Complications
As with any major surgery, there may be potential risks involved, such as the following:
- Anesthetic complications such as nausea, dizziness, and vomiting
- Infection of the wound
- Dislocation, requiring repeat surgery
- Damage to blood vessels, nerves, or muscles
- Failure to relieve pain
- Pulmonary embolism
- Wear and tear of the prosthesis
Summary
Shoulder replacement surgery involves replacement of the shoulder joint with artificial components to relieve pain and provide improved mobility of the shoulder joint when other conventional methods fail to provide relief. As with any surgery, shoulder replacement also has risks and complications. It is important you thoroughly discuss both its risks and benefits with your surgeon before undergoing the surgery.