Conjunctivitis
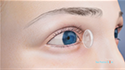
Conjunctivitis, commonly referred to as pinkeye, is a common condition affecting one or both eyes. It is characterized by inflammation of the conjunctiva, the mucous membrane covering the white of the eyes and the inner surface of the eyelids. Conjunctivitis may resolve on its own but sometimes requires treatment. It does not cause any permanent eye or vision changes.
Causes.
Conjunctivitis most often results from a viral infection. Other causes include bacteria, allergy to dust or pollen, exposure to irritants such as smoke, dirt or certain shampoos, as well as prolonged use of contact lenses. Infectious conjunctivitis is highly contagious so precautions should be taken to avoid spreading the condition to others.
Signs and Symptoms.
Common symptoms of conjunctivitis include redness of the eyes and pain with swelling of the eyelids. There may also be excessive tear flow and thick yellow-colored discharge from the eyes. The eyelids may become sticky with crust formation noticed especially on arising from sleep. You may also experience itchiness, blurry vision and increased sensitivity to light.
Diagnosis.
Your doctor will diagnose conjunctivitis based on your symptoms and a physical examination of the eyes. Fluid discharge may be obtained with a swab of the conjunctiva and sent to the laboratory for analysis. This helps your doctor find out the type of infection to decide on the appropriate treatment.
Treatment.
The treatment for conjunctivitis depends on its cause.
Viral conjunctivitis does not usually require treatment and symptoms should fade in about 2-3 weeks as the infection resolves. Antiviral medications may be prescribed.
In cases of bacterial infection, your doctor will prescribe antibiotic medications in the form of eye-drops or ointment.
Warm compresses applied over the eye may help soothe your symptoms if you have viral or bacterial conjunctivitis.
Allergic conjunctivitis responds to anti-allergic medicines such as antihistamines, steroids, ant-inflammatory drugs and decongestants. Cool compresses may also be helpful. Avoiding the substance that causes your allergic symptoms whenever possible is often the best solution to preventing allergic conjunctivitis.
Prevention.
Maintaining good hygiene helps prevent the spread of conjunctivitis. Wash your hands often and do not touch or rub your eyes. Avoid sharing towels or eye cosmetics. Change the pillow covers and bed linens frequently. If you use contact lenses, handle them carefully and follow a proper cleaning regimen.