Egg Freezing
Egg freezing is an assisted reproductive technique that allows a woman to preserve her eggs for later use. One of the reasons a woman may opt for egg freezing is to preserve her fertility after being diagnosed with cancer. Various cancers and their treatments can adversely affect a woman’s chances of conceiving.
Effects of Cancer Treatment on Fertility.
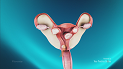
Cancer and the associated treatments can stop the production of certain hormones dramatically reducing your supply of eggs, or may damage reproductive organs such as the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus, thereby affecting fertility and leading to early menopause. Cancer treatment, including chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery (cancer-affected reproductive organ is removed) can lead to infertility.
Indications.
Egg freezing may be considered if:
You have been diagnosed with cancer and have 2-6 weeks’ time before you begin treatment.
Family history or risk of early menopause.
Genetic conditions such as BRCA mutations where ovarian removal is recommended.
Severe endometriosis.
Egg freezing is also considered for women who wish to delay pregnancy for reasons of concentrating on their career, education and other personal goals. It may be opted by those who have a religious objection with regard to embryo freezing and for couples undergoing fertility treatment in which the male partner is unable to provide sufficient sperm on the day of retrieval.
Procedure.
Egg freezing involves three primary steps:
Induction of ovulation.
Retrieval of the eggs.
Freezing.
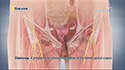
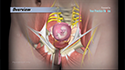
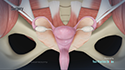
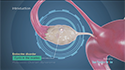
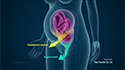
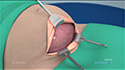
Your doctor first stimulates the ovaries by injecting synthetic hormones to boost the production of multiple eggs. Transvaginal ultrasound aspiration, a minor surgical procedure is performed under sedation to remove the eggs from the ovaries. A needle is guided through the vagina with an ultrasound probe and the eggs are removed with the help of a suction device attached to the needle. Soon after collection, the unfertilized eggs are frozen at sub-zero temperatures with a slow freeze, vitrification or cryoprotectants to avoid the formation of ice crystals. Eggs can be stored for up to 10 years.
When the eggs are required, the frozen eggs are thawed and allowed to fertilize with the sperm in the lab or sperm is directly injected into the egg via an intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) procedure, and implanted via in vitro fertilization (IVF) in the womb.
Advantages & Disadvantages.
Egg freezing helps preserve fertility until you are healthy enough or ready to conceive. The advantage of egg freezing, especially in young women, is the frozen egg retains the quality of eggs produced at a younger age, even while your age continues to advance.
Disadvantages of egg freezing include:
Expensive procedure.
Can delay cancer treatment and may not be an option for all women.
Some eggs may not survive the egg process of freezing and thawing. This affects the number of cycles of IVF.
Risks and complications.
As with any procedure, egg freezing may involve certain risks and complications which include:
Bloating.
Vomiting.
Infection.
Mild abdominal pain.
Nausea.
Diarrhea.
Bleeding.
Rapid weight gain.
Difficulty breathing.
Emotional disappointment with failure of the treatment.
Egg freezing may be a ray of hope for women diagnosed with cancer or other medical conditions that affect their ability to conceive. It provides the potential to conceive even after the toxic effects of the disease and its treatment are completed. However, it is not a guarantee for a successful pregnancy as it still involves certain risks. Please talk to your doctor to learn whether this procedure is right for you.