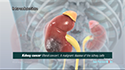
Kidney Tumors
A tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue found in the body. Tumors that are found attached to or in the kidneys are known as kidney tumors. Kidney tumors, also called renal tumors, may be benign (noncancerous) or malignant (cancerous). A benign kidney tumor is an abnormal growth of kidney cells that form a mass, but do not spread to other parts of the body, and are usually not life-threatening. Malignant kidney tumors occur when kidney cells become cancerous and grow out of control, forming a mass. The cancer cells invade and kill nearby tissues and spread to other parts of the body.
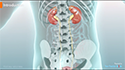
Kidney Anatomy
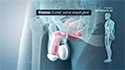
Kidneys are part of the urinary system and are the bean-shaped pair of organs located on either side of the spine in the lower back. The major function of the kidneys is to cleanse the blood of waste products and excrete them from the body in the form of urine.
Types of Kidney Tumors
Benign and malignant kidney tumors can be further divided into types:
Types of benign kidney tumors include:
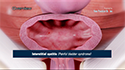
- Renal adenoma: Adenomas are the most common form of solid, benign kidney tumors, and are usually small, low-grade growths.
- Renal oncocytoma: Oncocytomas are benign, typically asymptomatic tumors that can become large. They can spread throughout the body and are not confined to the kidneys.
- Angiomyolipoma: Angiomyolipomas are rare, benign tumors composed of blood vessels, smooth muscle and fat, that can occur from an inherited genetic mutation.
- Fibroma: Fibromas are tumors of the fibrous tissue in, on, or surrounding the kidney.
- Lipoma: Lipomas are rare kidney tumors arising in the fat cells inside the kidney capsule or surrounding tissue.
Malignant Kidney Tumors
The two main types of malignant kidney tumors are renal cell carcinomas (RCCs) and transitional cell carcinomas (TCCs). RCCs are the most common malignant kidney tumors, and are located in the lining of the small tubes in the kidney. TCCs are far less common and typically occur in the urinary system. Wilms’ tumor, another type of malignant kidney tumor, is most commonly seen in children.
Causes
The exact cause of kidney tumors is unknown. There are certain factors that may increase the risk of developing kidney tumors such as smoking, prolonged dialysis treatment, family history of the disease, high blood pressure, obesity, and von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (VHL), a hereditary disease. Occupational exposure to certain substances and chemicals may also raise the risk for kidney tumors.
Signs and Symptoms
Tumors of the kidney may not produce symptoms immediately but may be detected during the evaluation of another problem or during a regular check-up. The spread of the tumor into the neighboring organs causes symptoms such as blood in the urine, fever, anemia (a low red blood cell count), loss of appetite, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, and pain in the lower back. Depending on the organ it spreads to, kidney tumors can cause other related symptoms.
Diagnosis
Over half of kidney tumors are detected by chance. Often, they are discovered during generic screening or when you visit a doctor for some other problem. To confirm the diagnosis of a kidney tumor, your physician may perform the following examinations or tests:
- A complete medical history and physical exam
- A complete blood count test (CBC) to check the blood for signs of disease
- A basic or complete metabolic panel (CMP) to check organ function
- Urinalysis to check for blood, infection, or protein in the urine
- Serum creatinine levels or other kidney function tests to determine if the kidneys are functioning normally
- MRI and CT scanning to help diagnose and stage kidney tumors
- Ultrasound to obtain detailed images of your kidneys
- A chest x-ray or bone scan to check if the cancer has spread
- A kidney biopsy to help identify the type of tumor you have
Treatment
Treatment for kidney tumors varies based on malignancy or non-malignancy of the tumor, severity, kidney function, and patient age. Some common treatment methods include:
Conservative Treatment
- Active Surveillance: In this method, your doctor will not provide treatment directly, but instead will analyze any tumor smaller than 3 cm at regular intervals and follow a “wait and watch” approach.
- Thermal Ablation/Cryotherapy: This involves the destruction of the tumor cells using heat or cold.
- Chemotherapy: Medication is given orally or intravenously to destroy the tumor.
- Radiation Therapy: High-energy external beams of radiation are directed into the body to destroy cancer cells.
- Immunotherapy: Also known as biologic therapy, this is a method that boosts your body's natural immunity to destroy the tumor.
Surgical Treatment
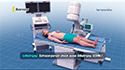
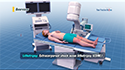
If conservative methods fail to improve symptoms, surgery is recommended. Surgery may be performed either as a minimally invasive laparoscopic surgery or as an open surgery and may include:
- Laparoscopic Nephrectomy (key-hole surgery): This is a minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves 3 to 4 small key-hole incisions and removal of the tumor and the kidney affected by the tumor.
- Partial Nephrectomy: This surgery involves the removal of the tumor or a portion of a kidney while the healthy tissue is left intact.
- Radical Nephrectomy: This involves the removal of the whole kidney along with the surrounding fatty tissue, lymph nodes, and adrenal glands.
Most healthy patients without comorbidities can continue to live a healthy life with the remaining kidney.
Summary
The human body has two kidneys that filter blood of waste and excrete it out of the body as urine. When abnormal growth of kidney cells occurs it is called a kidney tumor. The tumor may be limited to its origin or may affect the entire organ and spread to the neighboring tissues and lymph vessels. With timely intervention and a healthy lifestyle, kidney tumors can be successfully managed.