PEG/PEJ Procedure
When a medical condition interferes with the body receiving the nutrients it requires, your physician may recommend a PEG or a PEJ tube procedure to deliver the necessary nourishment.
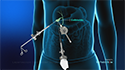
The two procedures vary only from the point of tube placement. A PEG (percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy) is a surgical technique for inserting a gastrostomy tube in the stomach. The word percutaneous refers to “through the skin,” and an endoscope is utilized to help place the PEG tube correctly. A PEJ (percutaneous endoscopic jejunostomy) procedure is similar to the PEG procedure, except that the tube is placed into the intestine (jejunum) instead of the stomach. A PEJ is considered long-term, difficult to maintain, and utilized less frequently than a PEG tube.
Indications
PEG tubes and PEJ tubes are feeding tubes that are indicated when you are unable to eat or drink as a result of conditions such as:
- Stroke or other brain injury
- Surgery of the head and neck
- Upper gastrointestinal tract neoplasm
- Dysphagia or difficulty swallowing
- Oropharyngeal and esophageal problems
Preparation
Preparation for the PEG or PEJ procedure may involve the following steps:
- A thorough history and physical examination
- Routine blood work and imaging
- Informing your doctor of any conditions you have such as diabetes, a heart or lung condition, bleeding risk, or allergies to medications or anesthesia
- Informing your doctor of any medications or supplements you are taking
- Refraining from medications such as blood thinners, aspirin, or NSAIDs, if indicated
- Refraining from solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to the procedure
- Arranging for someone to drive you home after the procedure
Surgical procedure
A PEG or PEJ procedure may involve the following steps:
- You will generally receive intravenous (IV) antibiotics and anesthesia. The anesthesia ensures that you remain numb and calm during the procedure, whereas the antibiotics prevent infection.
- A local anesthetic injection may also be given to numb the area where your surgeon makes the incision.
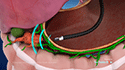
- A small incision is made on the abdomen, and a long, flexible instrument with a light and a camera at the end called an endoscope is used to guide the feeding tube through the incision. Endoscopy enables your physician to see the inside of your stomach and intestine.
- A PEG is a feeding tube that is placed into your stomach, whereas a PEJ tube is placed in your jejunum (the second part of your small intestine).
- PEG tubes allow nutrition, fluids and/or medications to be given directly into the stomach, bypassing the mouth and esophagus, whereas a PEJ tube allows nutrition, fluids and/or medications to be given directly into the jejunum bypassing the mouth, esophagus, and stomach.
- Finally, the scope and instruments are withdrawn, and the incision is closed with a small bandage.
Postoperative care
A postoperative dressing will be placed over the tube site insertion. This dressing will be removed within a day or two after the procedure. The PEG or PEJ tube site should be cleaned once a day with diluted soap and water. Between cleanings, the site should be kept dry. Usually, no special dressing or covering is needed. After the area around your feeding tube heals, you will meet with a dietitian who will explain how to use the feeding tube. Feedings will start slowly with clear liquids and be advanced accordingly. You may notice pain and drainage from the incision site or cramping from gas buildup in your digestive system. Medications are provided as needed to address these. A follow-up appointment will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Risks and Complications
Risks and complications of a PEG or PEJ tube insertion include:
- Infection
- Pain
- Aspiration
- Tube dislodgement
- Bleeding and perforation
- Leakage around the tube
Summary
A PEG or PEJ tube procedure is a safe and effective method of feeding and providing nutritional support for patients having problems with their gastrointestinal system. The entire procedure takes about 30 minutes, and you may return home the same day or the next morning. The feeding tube requires regular cleaning and drying between cleanings. Contact your health care provider for any questions regarding the maintenance and performance of your PEG or PEJ tube.