Laparoscopic Fundoplication
Laparoscopic fundoplication, also referred to as laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication, is a minimally invasive surgery commonly employed for the treatment of patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
GERD occurs when stomach contents reflux (flow backward) and enter the lower end of the esophagus due to a relaxed or weakened sphincter. This sphincter, called the LES or lower esophageal sphincter, is the valve between the esophagus and the stomach.
Normally, the stomach contents do not enter the esophagus (food pipe) due to a constricted LES. In GERD, the LES is weak or relaxed enabling stomach acids to reflux into the esophagus.
Laparoscopic fundoplication is a minimally invasive procedure that is performed to restore the function of the lower esophageal sphincter by wrapping the stomach around the distal end of the esophagus. This procedure creates a new “functional valve” between the esophagus and the stomach and prevents reflux of the acid and bile (non-acidic fluid) from the stomach into the esophagus.
Indications
Your surgeon may recommend laparoscopic fundoplication if your GERD is unresponsive to conservative treatment such as medication and lifestyle modification, and is causing GERD complications, such as:
- Heartburn
- Regurgitation
- Dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)
- Chronic esophagitis (inflammation of the esophagus)
- Barrett’s esophagus (damage of the esophagus lining)
- Peptic stricture (tightening or narrowing of the esophagus)
Laparoscopic fundoplication may also be indicated for the treatment of other conditions such as symptomatic hiatal hernia or extra-esophageal symptoms like hoarseness, asthma, chest pain, cough, and aspiration.
Preparation
Preoperative preparation for laparoscopic fundoplication may involve the following steps:
- A thorough history and physical examination
- Routine blood work and tests such as barium X-rays and endoscopy
- Informing your doctor of any allergies to medications or anesthesia
- Informing your doctor of any medications or supplements you are taking or any conditions you have such as heart or lung disease
- Refraining from certain medications, such as blood thinners or anti-inflammatories
- Refraining from solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to the procedure
- Arranging for someone to drive you home after the procedure
Surgical procedure
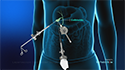
Laparoscopic fundoplication surgery is performed with a laparoscopic technique under general anesthesia.
A laparoscope is a small fiber-optic viewing instrument made up of a tiny lens, light source and video camera. The camera attached to the laparoscope displays the image of the abdomen on a monitor, allowing the surgeon to view the internal structures.
During the surgery, your surgeon makes small incisions known as portals in the abdomen. Through one incision, the laparoscope is introduced to view the abdomen. Along with the laparoscope, CO2 gas is used to expand the abdominal cavity, giving the surgeon a clear space to operate.
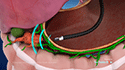
The other portal is used for the insertion of surgical instruments to carry out the required repair. With the images from the laparoscope as a guide, your surgeon wraps the upper part of the stomach, the fundus, around the lower esophagus to create a valve, suturing it in place. This reinforces the lower esophageal sphincter’s ability to close and helps to prevent gastroesophageal reflux from occurring. The laparoscope and other instruments are removed, and the tiny incisions are closed and covered with small bandages to complete the procedure.
Postoperative care
After the procedure, you will be transferred to the recovery room where your nurse will monitor your vital signs as you recover from the effects of anesthesia. You may be required to stay in the hospital for a day or two. You will be given pain medications to keep you comfortable and antacids to reduce the amount of acid produced by your stomach. Your surgeon may recommend that you follow certain measures for a successful outcome. These include:
- Avoid lifting heavy objects and activities that put excessive pressure on the abdomen.
- Drink plenty of liquids and eat only soft foods for 2 to 4 weeks following surgery.
- Do not remove the dressings over the incisions for the first two days and keep the area clean and dry. No showering or bathing during this time.
- Refrain from smoking and alcohol for a specific period of time, as these can hinder the healing process.
- Strict adherence to follow-up appointments is necessary to monitor your progress.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgery there are potential risks and complications involved. These include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Stomach bloating
- Swallowing difficulties
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Injury to blood vessels or organs
- Allergic/anesthetic reactions
Benefits
The benefits of laparoscopic fundoplication over open surgery include:
- Smaller incisions
- Faster healing
- Less pain
- Shorter recovery time
- Less scarring
- Minimal blood loss
- Minimal muscle trauma
Summary
Laparoscopic fundoplication is a surgical procedure to treat gastroesophageal reflux disease. If you have acid reflux that has not responded to medication or other conservative treatment, your physician may recommend this minimally invasive surgery. Laparoscopic fundoplication utilizes smaller incisions and results in a faster recovery. Most patients who undergo laparoscopic fundoplication experience a great deal of improvement in their GERD symptoms.