Gastritis
The lining of the stomach produces acid and enzymes to help in digestion of food. To protect itself from the acids, the stomach lining also produces a thick layer of mucus.
Gastritis is a condition where the stomach lining becomes inflamed and produces less acid, enzymes and mucus. Severe inflammation of the stomach lining that lasts for a day or two is called acute gastritis, while inflammation that develops slowly and lasts for a long time is referred to as chronic gastritis.
Causes.
The causes of gastritis include:
Helicobacter pylori bacterial infection.
Overuse of Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
Excessive alcohol consumption.
Stress.
Backflow of bile from the small intestine into the stomach.
Digestive disorders such as Pernicious anemia.
Exposure to radiation.
Traumatic injuries, severe burns, critical illness and major surgeries.
Signs and Symptoms.
The signs and symptoms of gastritis include:
Nausea or stomach upset.
Abdominal bloating or pain.
Indigestion.
Gnawing or burning feeling in the stomach.
Loss of appetite.
Vomiting blood.
Black, tarry stools.
Diagnosis.
Your doctor will ask question regarding yours and your family’s medical history and conduct a complete physical examination.
Diagnostic tests for gastritis include:
Blood, stool and breath tests for detecting the presence of Helicobacter pylori infection.
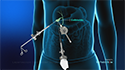
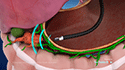
Endoscopy: Your doctor passes a narrow tube attached to a lens (endoscope) through your throat into the stomach and upper intestine to check for inflammation.
Biopsy: During endoscopy, a tissue sample of the stomach lining is removed and tested in the lab for the presence of inflammatory cells and damaged epithelium. Helicobacter pylori infection can also be detected from biopsy.
Barium swallow test: You will be given a white, metallic liquid (containing barium) to swallow, which will coat your digestive tract followed by X-rays. Ulcers and other abnormalities can be clearly detected through X-ray imaging.
Fecal occult blood test: Your doctor will check for the presence of blood in your stool.
Treatment.
Your doctor treats gastritis based on its cause.
Treatment for gastritis includes:
Treating the bacterial infection
with a combination of antibiotics.
Blocking acid producing cells
with proton pump inhibitors.
Reducing acid production
with histamine blockers.
Antacids to neutralize the stomach acids and provide pain relief.
Vitamin B12 supplements to treat pernicious anemia.
Apart from these interventions, you should avoid hot and spicy food and food that causes irritation such as lactose from dairy products or gluten from wheat. You should also stop prolonged use of NSAIDS and alcohol.
Gastritis is a common gastrointestinal problem that can cause severe pain and discomfort. Early and efficient treatment of the condition with simple lifestyle changes and other medications goes a long way in preventing the development of serious complications such as peptic ulcers and cancer. You should consult your doctor if you experience the symptoms of gastritis, so that your doctor can administer specific therapy for treating the underlying cause.