Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration (EUS-FNA)
Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration (EUS-FNA) is a minimally invasive diagnostic procedure that combines the use of an endoscope, a flexible tube-like device with an attached camera and light source, ultrasound imaging to examine the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and surrounding tissues and organs, and a fine needle to aspirate or remove suspicious tissue for evaluation and diagnosis.
The use of ultrasound enables physicians to view structures and organs not typically visible with endoscopy, such as the layers of the gastrointestinal tract wall. Ultrasound also assists with identification of any suspicious tissue lesions and accurate placement of the needle for removal of the tissue.
Indications
The endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration procedure may be used for the assessment of conditions pertaining to the GI tract.
The GI tract, also known as the alimentary canal or digestive tract, is a pathway or route through which food enters the body and solid wastes are expelled. The GI tract includes the mouth, throat, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, and anus.
Your physician may recommend an EUS-FNA to evaluate and diagnose GI conditions, such as:
- Pancreatic cysts or masses
- Lymph nodes (associated with suspected or known lymphoma or cancer)
- Submucosal masses
- Small liver lesions
- Intra-abdominal/intra-pleural fluid
- Duodenal (first part of the small intestine) biopsy for suspected malabsorption
- Abnormalities or tumors in the GI tract
- Colon cancer, esophagus cancer, pancreatic cancer, lung, or stomach cancer, and ampullary and rectal cancers
Preparation
Preoperative preparation for an endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration procedure may involve the following steps:
- You will be asked to fast for at least 6 hours before the test and make sure your stomach is empty.
- You may be asked to take a laxative or enema and to follow a liquid diet before the procedure.
- Your doctor should be informed of any chronic medical conditions like diabetes or high blood pressure.
- Your doctor will instruct you on the use of your regular medications prior to the procedure.
- You may need to stop taking certain medications, such as blood thinners as they can increase your risk of bleeding.
- You will need to inform your doctor of any allergies to medications or latex.
- An informed consent form will be obtained after the procedure has been explained.
Surgical procedure
In general, an endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration procedure will involve the following steps:
- You will lie on your back on the procedure table and be given a sedative medication.
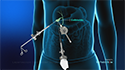
- An endoscope with an ultrasound probe and biopsy needle at the end is inserted through the mouth for upper GI endoscopy.
- For lower GI endoscopy, the endoscope will be inserted through the anus.
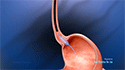
- The endoscope is guided to the area of concern and a small ultrasound device, known as a transducer or ultrasound probe, located on the tip of the endoscope, is activated to produce sound waves that create precise images of the surrounding tissue, which are viewed on a monitor.
- Under continuous real-time ultrasound guidance, a thin needle attached at the end of the endoscope is advanced into the area of suspicious GI structures to obtain an aspirate of the tissue. This technique is known as fine needle aspiration (FNA).
- The aspirated cells obtained from the FNA are smeared on a slide and analyzed under a microscope for abnormalities, such as tumors or cancer. This cell analysis is known as cytology.
Postoperative care
Following the procedure, you will be transferred to the recovery room where you will be monitored until the sedative wears off. If you had an upper GI EUS, you may experience a sore throat and minor cramps. Pain medications are prescribed as needed to address these discomforts. You may resume eating after the procedure unless instructed otherwise. You can start with a soft diet and slowly advance to solid foods as per your comfort level. EUS-FNA is usually performed in a clinic or office setting as an outpatient procedure, so you will be discharged home on the same day after a few hours of observation.
Benefits
The benefits of an endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration procedure include:
- Accurate placement of the needle for sample collection
- Less invasive
- Less painful
- Recovery time is short, and patients can resume their normal activities afterwards
Risks and Complications
The risks and complications of an endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Pain and soreness in the throat
- Injury to the adjacent structures
Summary
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration (EUS-FNA) is an effective, reliable, and safe biopsy technique to obtain samples for histological or cytological examination, either as a primary procedure or in instances where other biopsy techniques have failed. EUS-FNA has proven to be of crucial value in the diagnostic evaluation of benign and malignant disorders, as well as in staging of malignant tumors of the GI tract and surrounding organs.