Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease
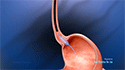
The esophagus is a narrow tube that passes food from the mouth to the stomach. At the junction of the stomach, the esophagus is surrounded by ring shaped muscles called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which acts as a valve, ensuring the one-way movement of food.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also called acid reflux or acid regurgitation, is a chronic disease of the digestive tract that occurs due to the spontaneous opening of the lower esophageal sphincter, which causes the backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus.
Occasional reflux of stomach acid is common, but reflux more than twice a week is considered serious and can lead to severe health issues.
Causes.
The causes of GERD include:
Abnormal relaxation of the lower esophageal sphincter.
Presence of hiatal hernia.
Obesity.
Pregnancy.
Smoking.
Certain medications such as painkillers, sedatives and antidepressants.
Signs and Symptoms.
The main symptom of GERD is a frequent burning sensation in the chest known as heartburn. Other signs and symptoms include:
Sour taste in the mouth.
Chest pain.
Swallowing difficulties.
Dry cough.
Hoarseness or sore throat.
Throwing up of food or sour liquid.
Diagnosis.
If you experience frequent heartburn, your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms. To confirm the diagnosis of GERD, other tests may be ordered such as:
Barium swallow radiograph: You will be given a chalky solution to swallow, which coats the lining of your digestive system,and can be visualized by X-ray imaging. This test helps your doctor check for hiatal hernia and other structural abnormalities of the esophagus.
Endoscopy: Your doctor inserts an endoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera, down your throat to examine the surface of your esophagus for any abnormalities.
Biopsy: A tissue sample can be collected through the endoscope and sent to the lab for examination of the esophagus cells under a microscope to assess for damage caused from acid reflux.
pH and impedance monitoring: This is the most accurate test to detect GERD. Your doctor will insert a small tube through the nose into the esophagus, to measure the amount of acid that enters the esophagus.
Treatment.
Treatment of GERD will depend on the severity of your condition. Your doctor may suggest one or more treatment approaches which include:
Lifestyle changes
You will be instructed to stop smoking, lose weight if overweight, eat small frequent meals, and avoid GERD triggers such as fried, spicy food, alcohol and caffeine. You should also avoid lying down immediately after meals and keep your head elevated while sleeping.
Medications may be prescribed to neutralize the stomach acids, decrease acid production, and heal the damaged esophageal lining.Surgery.
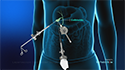
Your doctor may recommend surgery if lifestyle changes and medications fail to manage the symptoms of GERD. Two types of surgeries can be performed.
Nissen fundoplication:
In this surgery, your surgeon will wrap the top of the stomach around the lower esophagus in order to tighten the lower esophageal sphincter.
Stretta procedure:
In the stretta procedure, the esophageal tissue is heated with radiofrequency energy to create scar tissue. The scars help strengthen the esophageal muscles.
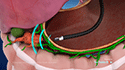
Linx Procedure:
A ring of tiny magnetic titanium beads called a Linx device is inserted around the lower esophageal sphincter. The device closes the LES opening to prevent acid reflux due to magnetic attraction between the beads, but opens up to allow the passage of food through it.
The most common symptom of GERD is frequent heartburn. You should consult your doctor if GERD is present for more than 2 weeks in spite of taking antacids. If lifestyle changes and medications do not resolve the symptoms of GERD, your doctor may suggest surgery.