Hair Transplantation
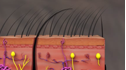
Hair transplantation, also referred to as hair replacement or hair restoration, is a surgery most commonly employed to restore hair to areas with hair loss, such as the scalp. This is achieved by transplanting (moving or transferring) hair from an area of thick growth such as the back or side of the head to the front or top of the head.
Indications
Hair transplantation is typically indicated as a treatment for hair loss. Hair loss refers to the loss of hair from the scalp or body. Hair loss in the scalp can range from mild hair thinning to total baldness. Hair can fall out due to various reasons such as hormonal changes, heredity, medications, or medical conditions. It may be temporary or permanent and is more common in men than women.
Who is a Good Candidate for Hair Transplantation?
Hair transplantation surgery can remarkably improve your appearance and sense of well-being. However, not everyone is a good candidate for surgery. Candidates suitable for hair transplantation surgery include:
- Men who have lost hair due to male pattern baldness over the last 5 years
- Men with balding patterns that have stabilized for many years
- Men who have realistic expectations about the surgery and who understand that hair loss might continue despite surgery
- Men and women who have suffered trauma or burns causing hair loss
- Men and women who have lost hair due to cosmetic procedures
Preparation
In general, hair transplantation surgery may involve the following:
- A review of your medical history and a physical examination
- Routine blood work and imaging
- Informing your doctor of any medications or supplements you are taking
- Refraining from medications such as blood thinners or anti-inflammatories
- Informing your doctor of any allergies to medications, anesthesia, or latex
- Refraining from solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to the procedure
- Informing your doctor of any recent illnesses or other medical conditions
- Arranging for someone to drive you home after the procedure
- Signing an informed consent form
Surgical procedure
Most hair transplants are performed in a doctor's office. In general, the procedure involves the following:
- Your surgeon will administer a local anesthetic to numb the scalp area. You may also receive medications to relax you.
- Your scalp is thoroughly cleaned.
- A strip of scalp with hair is removed using a surgical knife (scalpel) and kept aside. This area of your scalp is known as the donor area. The scalp is then closed with tiny stitches.
- Individual hairs or small groups of hairs are carefully separated from the removed scalp.
- In some instances, smaller areas of the scalp and groups of hairs are removed with other equipment or robotic assistance.
- The bald areas that will receive these healthy hairs are thoroughly cleaned. These areas of your scalp are known as the recipient areas.
- Tiny cuts are made in the bald area, and healthy hairs are carefully placed in these cuts.
- Once all the hairs have been transplanted, your scalp will be sutured and bandaged.
- Your stitches will be removed about 10 days after surgery.
A hair transplant session may take 4 hours or more. During a single treatment session, hundreds or even thousands of hairs may be transplanted. You may need up to 3 or 4 sessions to achieve the full head of hair you desire.
Postoperative care
Hair transplantation is typically performed as an outpatient surgery, meaning you can go home the same day. In general, postoperative care instructions will involve the following:
- After the surgery, your scalp may feel sore and tender. Pain medications are provided for several days to address this.
- Your physician may also prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs to manage swelling and antibiotics to reduce the risk of infection.
- You may also experience mild bleeding for a few days after surgery. Applying pressure gently on the area for about 15 minutes with a gauze pad should be sufficient to stop the bleeding.
- Most patients can return to work in 2 to 5 days after a hair transplant.
- Instructions on surgical site care will be given, and hair care recommendations provided, such as washing your hair gently the day following the surgery, gently combing the hair for a week, and refraining from hair dryers, hairspray, hair color products, and haircuts for at least a couple of weeks.
- Do not swim in chlorinated water for at least a couple of weeks and refrain from any strenuous activities or sports for a week.
- Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Risks and Complications
The risks and complications associated with hair transplantation may include:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Bruising
- Swelling
- Soreness
- Inflammation
- Numbness
- Unnatural-looking tufts of hair
Summary
Hair transplantation is a surgery to transfer hair from hair-rich areas to bald areas. Most people who have a hair transplant have male or female pattern baldness. Hair transplantation can improve the appearance and self-confidence of those who are balding and enhance their overall quality of life.