Angiogram
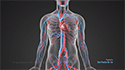
Blood transports life-sustaining oxygen and other essential nutrients to all parts of the body. Blood flows through tiny vessels called arteries and veins. Defects in these blood vessels can interrupt the flow of blood.
Abnormal blood vessels can be detected by angiogram. An angiogram is an imaging test that uses a special dye and X-ray images to take pictures of blood flow in arteries and veins.
There are several types of angiograms named after the body part to be viewed:
Coronary angiogram: heart vessels
Pulmonary angiogram: lung vessels
Carotid angiogram: Head and neck vessels
Peripheral angiogram: arm and leg vessels
Aorta angiogram: aortic vessels
An angiogram may be referred to as an arteriogram when the arteries are studied, and a venogram when the veins are studied.
Indications.
An angiogram may be indicated for the diagnosis of:
Aneurysms, bulging, weakened areas along an artery
Blood flow pattern to a tumor
Renal artery conditions
Peripheral artery disease or PAD
Atherosclerosis, plaque buildup in arteries
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT), blood clot in the leg
Blood clots in lungs (pulmonary embolism)
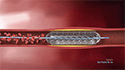
In case of narrowed arteries due to plaque buildup atherosclerosis, the angiogram is often combined with another procedure called Angioplasty. In angioplasty a catheter with a balloon attached to the end of it, is inserted into the artery and inflated to open up the blockage for better blood flow.
Pre-procedural preparation.
Before an angiogram, inform your doctor if you are pregnant, breast-feeding, asthmatic, have bleeding problems, or any allergies to iodine dye, bee stings or shellfish. Your doctor will ask you about the medicines you are taking, and review your history. Your doctor may order certain blood tests, and will advise you not to eat or drink for 4 to 8 hours before the procedure. You will be asked to empty your bladder before the test begins.
Procedure.
The following steps are involved in performing an angiogram:
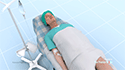
You will lie on your back on an X-ray table. Your doctor will insert an intravenous line in the vein of your arm to provide the required medicines and fluids.
A pulse oximeter will be placed on your finger or ear to measure the levels of oxygen in your blood. Electrodes will be placed on your arms, chest or legs to record your heart rhythm and heart rate.
The groin or region above the elbow where the catheter is to be inserted will be cleaned, shaved and numbed with a local anesthetic.
Your doctor will insert a guide wire through a needle into the blood vessel, after which the needle is removed. The catheter will then be inserted into the blood vessel over the guide wire and advanced to the area to be studied. A fluoroscope (real time X-ray) will be used to monitor the path of the catheter in the blood vessel.
The iodine dye will be injected through the catheter and many X-ray images will be taken. You will be asked to hold your breath for a few seconds. After the angiogram, the catheter will be removed and pressure applied on the needle site to stop bleeding. The site is then covered with a bandage. The entire procedure takes 1 to 3 hours to complete depending on whether other procedures are performed such as angioplasty.
Post-procedural Care.
Bed rest is recommended for several hours after the procedure.
Ice packs can be used to relieve pain and swelling over the needle site. You will also be prescribed medication to relieve any discomfort.
If the catheter was inserted in your arm, avoid blood tests and measuring blood pressure for several days after the procedure. If the catheter was inserted in the groin area, the leg should be kept straight for about 6 hours.
Risks and complications.
As with any procedure, angiogram includes potential risks and complications. These include:
Bleeding or clotting at the needle site
Kidney damage
Allergic reaction to the dye
Blood vessel damage
Risk of heart attack
An angiogram is a diagnostic imaging test used to detect blood vessel abnormalities in the body. Talk to your doctor about any concerns you may have regarding angiogram before undergoing the procedure.