Robotic Unicondylar Knee Replacement
A unicondylar knee replacement is a procedure to replace part of the knee joint with a prosthetic implant to relieve pain and improve function of the joint. Advances in technology have allowed this procedure to be performed in a minimally invasive manner with robotic assistance.
Indications
Knee replacement surgery is recommended for patients with osteoarthritis causing knee pain and disability that does not respond well to conservative treatments. Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease causing breakdown and eventual loss of cartilage in the joint enabling bones to rub against each other leading to painful movement.
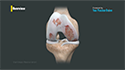
The knee can be divided into 3 compartments:
The medial compartment towards the inside of the knee, the lateral compartment towards the outside of the knee and the patellofemoral compartment between the kneecap and the lower end of the thighbone. Osteoarthritis usually begins in the medial compartment of the knee and may later advance to the other compartments. Early or mid-stage osteoarthritis involving just one compartment or one condyle may be treated by unicondylar knee replacement where only the affected joint surfaces are replaced.
Surgical procedure
The procedure can be performed on an outpatient basis but you may require a 1-3 day stay. Preoperative CT imaging is used to create a virtual 3-dimensional model of the knee. This information is fed into the robotic system and helps your doctor choose an appropriate implant and design a specific surgical plan. The procedure is performed with the robotic arm inserted through a 4-to 6-inch incision over the knee. Alignment of the knee and soft tissue balance are checked and the preoperative plan can be refined during the procedure. The robotic system provides your doctor with visual, audio and tactile feedback as the bone is cut and the implants positioned. This results in a high degree of precision, minimal damage to the bone and surrounding ligaments and accurate positioning of the implants, which is very important for a successful and long-lasting knee replacement.
Postoperative care
Following surgery, you may be able to leave the hospital on the same day if your doctor feels you have recovered well. Recovery depends on various factors but is generally quick. Physical therapy may be recommended. You are advised to maintain a healthy weight to minimize stress on the joint.
Benefits
Advantages of robotic unicondylar knee replacement includes:
- Small incision
- Less tissue injury
- Less bone removal
- Better implant positioning
- Shorter hospital stay
- Quicker recovery
- More natural feel to the knee
- A total knee replacement may be performed later if needed
Risks and Complications
As with any procedure, robotic unicondylar knee replacement is associated with certain risks which include infection, blood clots, nerve or blood vessel injury, implant loosening or fracture.
Summary
If osteoarthritis is affecting your quality of life and is limited to one portion of your knee, a robotic unicondylar knee replacement may be a suitable option for you. This highly precise operation preserves more bone and soft tissue, results in a natural feeling knee and offers a quick recovery with fewer complications.