Outpatient Knee Replacement
Outpatient knee replacement, also known as same-day or ambulatory knee replacement, refers to a surgical procedure where a patient undergoes knee replacement surgery and is discharged on the same day without an overnight hospital stay. Traditional knee replacement surgeries typically involve a hospital stay of one to several days for postoperative recovery and monitoring. In contrast, outpatient knee replacement aims to expedite the recovery process and reduce the overall cost of healthcare.
Several factors contribute to making outpatient knee replacement possible, including minimally invasive surgical approaches, improved pain management methods, and accelerated rehabilitation programs that help patients recover faster, making it feasible for them to go home on the same day as the surgery.
Anatomy of the Knee
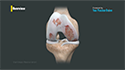
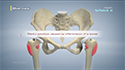
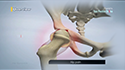
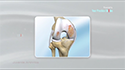
The knee is made up of the femur (thighbone), tibia (shinbone) and patella (kneecap). The lower end of the femur meets the upper end of the tibia at the knee joint. A small disk of bone called the patella rests on a groove on the front side of the femoral end. The fibula, another bone of the lower leg, forms a joint with the shinbone. The bones are held together by protective tissues, ligaments, tendons, and muscles. Synovial fluid within the joint aids in the smooth movement of the bones over one another. The meniscus, a soft crescent-shaped area of cartilage between the femur and tibia, serves as a cushion and helps absorb shock during motion.
Indications
Outpatient knee replacement is typically indicated for patients suffering from degenerative knee disease, such as osteoarthritis, that is not responsive to conservative treatment.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes breakdown and eventual loss of cartilage in the knee joint, making the bones rub against each other, leading to painful movement. Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn-out or damaged surfaces of the knee joint are removed and replaced with an artificial knee implant or prosthesis.
However, not all patients are suitable candidates for outpatient knee replacement. Some general factors that may make a patient a suitable candidate include:
- Age
- Good overall health
- Good social support
- No serious medical complications
- Healthy BMI (body mass index)
- Patient motivation and compliance
Preparation
Preoperative preparation for outpatient knee replacement includes:
- A comprehensive medical evaluation, routine blood tests, and imaging studies
- Informing your doctor of any allergies to medications, anesthesia, or latex
- Providing your physician with a list of any medications or supplements you are taking
- You may need to adjust or temporarily stop taking certain medications - especially those that can affect blood clotting
- Disclosing any recent illnesses or other medical conditions you may have
- Stopping smoking, as it can impact the healing process and increase the risk of complications
- Abstaining from food or drink for at least 8 hours prior to the surgery
- Signing an informed consent form
Surgical procedure
The outpatient knee replacement procedure is performed using advancements in anesthetic techniques like a femoral regional block that produces a centralized anesthetic effect and does not require a hospital stay as its effects wear off, as with traditional general anesthesia. The arthritic knee is approached through small incisions of three-to-four inches (compared to the eight-to-twelve-inch-long incision used in the standard open surgical technique), ensuring that the surrounding muscles and tendons are not cut. This facilitates a faster recovery. The damaged or arthritic knee joint surfaces are removed, and the artificial joint components (prosthesis) are implanted. With the new implant in place, the knee is taken through a series of range-of-motion movements. The muscles are then approximated, and the incision is closed and covered with a sterile dressing.
Postoperative care
After surgery, you will be transferred to the recovery area where you will rest until you are discharged. You will receive pain-relief medications as needed. You may have to wear stockings to prevent blood from pooling in your legs. You will be able to do light activities within a couple of weeks. You will also be given postoperative advice and instructions on the following:
- The use of assistive devices for walking, such as a cane or crutches
- Limited weight-bearing activities
- Suture and dressing care
- Strict adherence to a physical therapy and exercise regimen to improve knee range of motion and strengthen muscles
- Dietary changes and supplements to improve bone health
- Adherence to prescribed medications
- Adherence to follow-up appointments to monitor your progress
Benefits
The benefits of an outpatient knee procedure include:
- Minimal surgical dissection
- Faster recovery
- A shorter hospital stay
- A quicker return to an active lifestyle
- Lower risk of post-surgical complications
- Minimal muscle trauma
- Lower healthcare costs
Risks and Complications
Risks and Complications of outpatient knee replacement include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Knee stiffness/instability
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Allergic/anesthetic reactions
- Injury to nerves or blood vessels
Summary
Outpatient knee replacement surgery is similar to a traditional surgery, but involves advancements in surgical techniques, anesthesia, pain management, and rehabilitation protocols as compared to the traditional surgical approach. This type of surgery is less invasive to the tissues and bones, and involves a much shorter hospitalization time where the patient can go home the same day.