Robotic Total Knee Replacement
Robotic total knee replacement is a minimally invasive surgical procedure and an alternative to traditional knee replacement surgery that utilizes robotic-arm technology to improve accuracy and precision during a knee replacement.
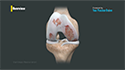
A robotic knee replacement is similar to a traditional knee replacement. Total knee replacement, also called total knee arthroplasty, is a surgical procedure in which the worn-out or damaged parts of the knee joint are removed and replaced with artificial knee joints called prostheses or implants. The difference with robotic knee replacement is that the procedure is performed with the assistance of a robotic arm or handheld robotic device that allows for greater precision in implant placement, and better results as compared to traditional surgery.
Indications
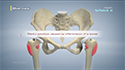
Robotic total knee replacement is indicated for partial or total knee replacement in patients suffering from degenerative knee disease, such as osteoarthritis, that is not responsive to conservative treatment.
Osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes breakdown and eventual loss of cartilage in the knee joint, making the bones rub against each other, leading to painful movement.
Preparation
The preoperative preparation for robotic total knee replacement is similar to traditional knee replacement procedures. But contrary to traditional knee replacement techniques, the robotic technique utilizes a series of CT scans to generate 3D images of an individual’s unique knee anatomy.
These images enable the surgeon to design a personalized plan based on the specifics of an individual’s knee anatomy prior to performing the surgery.
Additional pre-surgery preparation may involve the following steps:
- A thorough history and physical examination
- Diagnostic tests such as routine blood work
- Informing your doctor about medications or supplements you are taking
- Informing about allergies to any medications, anesthesia, or latex (which can be found in surgical gloves)
- Disclosing any recent illnesses or other medical conditions, which may impact the surgery
- Refraining from some medications such as blood thinners and supplements, if contraindicated for the procedure
- Refraining from solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to surgery
- Arranging for someone to drive you home following surgery
Surgical procedure
In general, a robotic total knee replacement procedure is similar to a traditional knee replacement but is performed with the help of a hand-held robotic system. The robotic system does not perform the procedure on its own. The surgery is performed entirely by your surgeon by prompting the robotic hands based on the surgeon’s personalized plan. The robotic surgical system is an additional tool to guide your surgeon to ensure greater accuracy in the placement of knee implants.
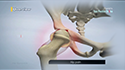
Robotic total knee replacement surgery is usually done under general anesthesia with you appropriately placed on the operating table. A 4 to 6 inch incision is made over your knee to expose the knee joint, as opposed to a 10 to 12 inch long incision required for a traditional total knee replacement. Supporting structures of the knee are gently moved out of the way, allowing removal of damaged cartilage and bone tissue from the surfaces of the femur and tibia. Using CT scans, the robotic arm can work from 3D images of the surgical area and perform a range of tasks, such as preparing the bone, introducing the implant, balancing the implant, and checking for the right fit. It utilizes a camera and optical trackers that are secured to the patient's leg to determine the exact position of the knee during surgery. The active robotic sensors map the replacement location and proceed with autonomous resection with the utmost precision. The machine alerts the surgeon to movement and guides them to place the prosthetics at the exact location. The muscles are then approximated, and the incision is closed and covered with a sterile dressing. The robotic system ensures that the surgical plan designed by your surgeon is carried out without any changes and with a high degree of precision.
Postoperative care
Following surgery, you will require pain management with medications and ice packs. Incision site care and bathing instructions will be provided to keep the wound clean and dry. You should refrain from strenuous and heavy lifting activities for a defined period. A knee brace or immobilizer may be recommended to protect the repair, depending on your surgeon’s preference.
The healing process may take anywhere from 8 to 12 weeks. You will require the use of crutches until you are able to walk without assistance. A physical therapist will teach you specific exercises to strengthen your leg muscles and restore knee movement. You should be able to resume your normal activities in a couple of months. Follow-up appointments will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Risks and Complications
Robotic total knee replacement is a relatively safe procedure; however, as with any surgery, there are risks and complications that can occur, such as:
- Pain
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Knee stiffness/instability
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Allergic/anesthetic reactions
- Injury to nerves or blood vessels
Advantages
Some of the benefits of robotic total knee replacement over traditional knee replacement include:
- Smaller incision
- Minimal postoperative pain
- Minimal muscle trauma/scarring
- Greater accuracy in implant placement
- Improved implant longevity
- Shorter hospital stay
- Rapid recovery
- Lower risk of revision replacement
- Higher patient satisfaction
Summary
Robotic total knee replacement is a minimally invasive procedure for knee joint replacement. The robotic system comprises state-of-the-art features, including real-time information to assist surgeons with bone resections, assessment of soft tissue conditions, and precise placement of the implant intraoperatively based on the patient’s unique knee anatomy.