Subtrochanteric Hip Fracture
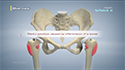
A hip fracture is a break that occurs near the hip in the upper part of the femur or thigh bone. The thigh bone has two bony processes on the upper part - the greater and lesser trochanters. The lesser trochanter projects from the base of the femoral neck on the back of the thigh bone. Hip fractures can occur either due to a break in the femoral neck, in the area between the greater and lesser trochanter or below the lesser trochanter.
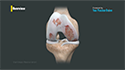
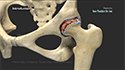
Subtrochanteric hip fracture is a break between the lesser trochanter and the area approximately 5 centimeters below the lesser trochanter. The fracture can be classified based on its location:
Type I occurs at the level of the lesser trochanter,
Type II occurs within 2.5 cm below the lesser trochanter and, Type III occurs between 2.5 and 5cm below the lesser trochanter.
Causes
A subtrochanteric hip fracture is most frequently caused from minor trauma in elderly patients with weak bones, and by high-energy trauma in young people. Long term use of certain medicines, such as bisphosphonates to treat osteoporosis (a disease causing weak bones) and other bone diseases, increases the risk of subtrochanteric hip fractures.
Signs and Symptoms
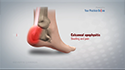
Signs and symptoms of subtrochanteric hip fracture include
Pain in the groin or outer upper thigh
Swelling and tenderness
Discomfort while rotating the hip
Shortening of the injured leg
Outward or inward turning of the foot and knee of the injured leg
Diagnosis
Your doctor may order an X-ray to diagnose subtrochanteric hip fracture. Other imaging tests, such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may also be performed to detect the fracture.
Surgery
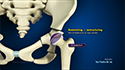
Surgery is usually the main treatment for subtrochanteric fractures. Surgical options include external fixation, intramedullary fixation or by using plates and screws.
External fixation is a temporary fixation and used for severe open fractures. Pins are inserted into each of the fractured fragments and supported with tubes close to the bone. The tubes are interconnected together with short tubes to provide more stiffness for the frame.
Intramedullary fixation involves managing the fracture with a long intramedullary nail which is fixed with a large screw. Additional screws known as interlocking screws are inserted at the lower end of the nail to prevent rotation of bones around the nail.
You surgeon may use a plate with screws attached instead of a nail in certain cases. Screws will be fixed into the bone from the outer side of the femur. A large screw will be inserted through the femoral neck and head, and other screws will be inserted across the length of the plate to hold the fracture together.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, surgery for a sub trochanteric fracture involves certain risks and complications including:
Non-union of fracture with pain
Limp or limited hip rotation due to malunion
Nail or screw fixation failure
Wound infection
Sub trochanteric fractures occur less commonly than other fractures and are considered the most difficult to treat. Your doctor will suggest an appropriate therapeutic approach to treat the fracture based on your age and the severity of the fracture.