Outpatient Hip Replacement
Outpatient hip replacement is also known as same-day hip replacement, rapid-recovery hip replacement, or ambulatory hip replacement.
Traditionally, joint replacement has been an inpatient surgical procedure at a hospital. With the introduction of minimally invasive techniques, modern pain-relief protocols, improved anesthetic techniques, and rapid rehabilitation protocols, surgeons are able to perform joint replacement procedures on an outpatient basis.
Outpatient hip replacement is the same as a traditional hip replacement, but the patient is allowed to go home in the first 24 hours after the surgery to recover at home.
The patient’s provider team and home support person, such as a spouse or friend, will closely monitor and provide support for the patient during the recovery process. The patient will closely follow and implement the postoperative protocols provided by their surgeon and care team from home.
In some cases, physical therapists are also available for in-home patient visits for several days to work with the patient on their range-of-motion and flexibility exercises.
Indications
Outpatient hip replacement is typically recommended for patients who meet certain criteria, such as:
- Are healthy without any major comorbidities
- Have a strong support system at home for assistance in the recovery process
- Are motivated to participate and complete the physical therapy program
- Do not have significant medical conditions that could complicate recovery
- Are non-smokers, as smoking can hinder the wound-healing process and increase postoperative pain.
Preparation
In general, preparation for outpatient hip replacement may involve the following:
- A comprehensive medical evaluation, including a review of your medical history, medications, allergies, blood tests, and imaging studies, to assess your overall health and suitability for the surgery.
- Instructions on preparing your home environment for return on the same day as the surgery. This may include stocking food supplies, toiletries, clearing the floors of any tripping hazards, and if possible, having living quarters on the same floor as the kitchen and toilet.
- Arranging assistance from a family member, friend, or hired helper who can help you recover at home.
- Abstaining from food or drink at least 8 hours prior to surgery.
- Planning for transportation to and from the hospital or surgical center the day of the surgery.
Surgical procedure
In general, the procedure for an outpatient hip replacement surgery may involve the following:
- You will typically be given regional anesthesia, such as spinal or epidural anesthesia, combined with sedation, to keep you comfortable and pain-free during the surgery.
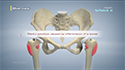
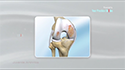
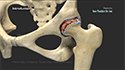
- Once you are under anesthesia, the surgeon makes an incision that is usually 6 to 8 inches long on the side of your hip.
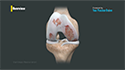
- The surgeon then carefully moves muscles and other tissues to access the hip joint. Specialized instruments are used to remove the damaged parts of the hip joint, including the damaged cartilage and bone.
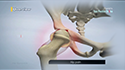
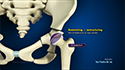
- After preparing the hip socket (acetabulum) and femur (thighbone), the surgeon inserts the artificial components of the hip implant. This typically includes a metal socket with a plastic liner for the acetabulum, and a metal or ceramic stem with a metal or ceramic ball for the femur.
- The components are secured in place with cement or through a press-fit technique.
- The incision is then closed in layers and a sterile dressing is placed on the surgical wound.
Postoperative care
After surgery, you are taken to a recovery area where you will be monitored closely as you wake up from the anesthesia. Vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels are monitored, and pain management is initiated as needed. Once you are awake and stable, you will begin working with physical therapists to start gentle exercises and mobility activities. Pain management strategies, including medications and ice packs, are used to keep you comfortable. If you meet specific criteria, such as being able to walk with assistance, having stable vital signs, and managing pain well, you may be discharged on the same day as the surgery. Instructions for home care, follow-up appointments, medications, and activity restrictions, will be provided.
Risks and Complications
Outpatient hip replacement surgery, like any surgical procedure, carries certain risks and potential complications. These include:
- Infection
- Blood clots (deep vein thrombosis or DVT)
- Implant issues
- Damage to nerves or blood vessels
- Pain and discomfort
- Functional limitations
- Anesthesia-related risks
Benefits
Outpatient hip replacement has several benefits over traditional hip replacement surgery. These include:
- Economical as there are no hospital room charges and related hospital charges
- Faster recovery compared to a patient undergoing inpatient surgery
- Reduced stress as lack of social interaction in a hospital can negatively affect your recovery
- Reduced risk of hospital-acquired infection (HAI)
- Improved patient satisfaction as it allows for recovering in a home setting in a familiar and comfortable environment, surrounded by family and support
- Shorter hospital stay
Summary
Outpatient hip replacement surgery is similar to a traditional surgery, but involves advancements in surgical techniques, anesthesia, pain management, and rehabilitation protocols as compared to the traditional surgical approach. This type of surgery is less invasive to the tissues and bones, and involves a much shorter hospitalization time where the patient can go home the same day.