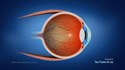
Cataract
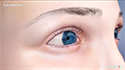
A cataract is a condition which causes
clouding of lens in the eye resulting in blurry
vision.
The lens is situated behind the iris, the dark
portion of the eye, and is not visible. When a
cataract occurs, the lens becomes cloudy and
is seen as a white cloudy ball in the center of
the iris.
The lens is made up of mostly water and
proteins. These specific proteins provide its
transparent structure. Any structural change
in these proteins can alter the clarity of the
lens and negatively impact vision.
There are three types of cataracts classified
according to their location in the eye.
Nuclear cataract is when the cloudiness is
present in the center of the lens.
With Cortical cataract, the cloudiness is seen
in the outer peripheral region or cortical
region of the lens.
Subcapsular cataract occurs at the back of the
lens capsule or subcapsular region. This type
develops quicker and can appear more
suddenly than the nuclear and cortical
cataract.
Cataracts are also classified according to the
cause, either as age related cataract,
congenital cataract, secondary cataract or
traumatic cataract.
A cataract can occur due to many reasons.
Age As people age, changes can occur in
the structure of the lens protein leading
to cataract.
Congenital causes-Cataract can occur in
newborns as inherited disorder or can
develop in infants because of infections in
mother during pregnancy such as rubella,
herpes simplex and syphilis.
Secondary causes- Cataract can form as a
complication of other diseases such as
glaucoma and diabetes. Prolonged use of
corticosteroid inhalers and eye drops
increases the risk of cataract.
Trauma Certain injuries may result in
formation of a cataract. Cataract may also
develop years after the injury.
Other causes include excessive exposure
of the eyes to UV rays, X-rays and other
radiation during radiotherapy.
Cataracts usually develop very slowly and are
not associated with any pain or redness of the
eye. Your vision gradually becomes blurred as
if you are looking through the dirty lens of a
camera. Some patients may see a halo around
bright lights. Others find the glare from the
sun and head lights of approaching cars at
night annoying. Some patients present with
double vision in one of the eyes and the colors
appear dull or muted. In others, frequent
prescription changes for glasses or contact lens may become necessary.To assess the impact of cataract on your
vision your doctor will perform a Visual Acuity Test where the patient reads an eye chart
from particular distance with one eye at a
time.
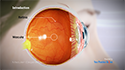
The doctor then examines the cornea, iris,
and lens individually using an intense ray of
light from a slit lamp to detect any
abnormalities.
For the retinal exam, eye drops are added to
dilate the eye and the retina is examined for
any abnormalities using an ophthalmoscope.
a cataract develops it cannot be cured
by eye drops or medication. Patients with
mild cataracts may be helped by using strong
bifocal glasses and using appropriate light
while reading.
Surgery is the only treatment for cataract and
is recommended based on the severity of the
disease and the impact on the daily activities
of the patient. The patient usually makes the
decision to have surgery when the symptoms
negatively impact their lifestyle.
Surgery is performed on one eye at a time
with a few weeks gap in between the two
operations. Cataract surgery is done on an
outpatient basis where the patient can go
home the same day. The eye and area around
the eye is numbed using local anesthesia. The
cloudy lens is removed and replaced with a
clear plastic lens in the same lens capsule as
the natural lens.
There are three types of surgical procedures
to treat cataract:
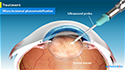
The most common procedure used is
Phacoemulsification where your surgeon uses
an ultrasound probe to break up the lens
which is then removed by suction. The
advantage is that the incision is very small,
around 3 to 5 mm, depending on the choice of
lens, foldable or non-foldable. The incision
heals on its own and does not require any eye
patch or stitches. This surgery takes less than
30 minutes.
The second type of surgery is extracapsular
cataract surgery. This is performed when the
lens is too dense and cannot be removed by
phacoemulsification. The incision is larger as
the complete lens is removed as a single
piece. The healing process for this type of
surgery is longer and requires an eye patch
temporarily over the eye after the surgery.
Intracapsular cataract surgery is rarely
performed and only in cases of severe trauma
to the eye. The incision is even larger than in
extracapsular surgery. The whole lens is
removed along with the lens capsule. The
clear plastic lens is then placed in front of the
iris rather than in the capsule.
The intraocular plastic lens used in this type
of surgery is chosen to provide the patient with
best possible correction. Three types of
intraocular plastic lenses monofocal, toric
and multifocal lens are used.
Following surgery your doctor will prescribe
eye drops to prevent infection and
inflammation. A follow up visit is scheduled to
monitor healing and to check for any
complications from surgery. Once complete
healing occurs glasses are ordered for optimal
vision, if required, depending on the type of
Cataract surgery is one of the safest surgeries
to undergo. Complications are rare but can
occur and need to be addressed as soon as
possible to prevent any vision loss.
Complications can include persistent
inflammation, infection, increase in
intraocular pressure, or peeling of the retina
at the back of the eye. In rare cases the
cataract seems to reappear after a few
months or years following surgery with a
cloudy appearance in the field of vision. This
occurs due to cloudiness of the capsule and
not the implanted plastic lens. It is called a
secondary cataract and can be treated by a
simple laser surgery to create a hole in the
lens capsule where the cloudiness is visible.
Cataracts may be prevented by
maintaining a healthy life style.
Fruits and vegetables are a good natural
source of vitamins and antioxidants
important in the normal growth,
functioning and prevention of age related
damage to the eye lens. A diet rich in
fruits and vegetables can help prevent
cataracts.
Not smoking or quitting if you do smoke
lowers your risk of developing cataracts.
Regular exercise and maintaining a
healthy body weight also helps to prevent
cataracts.
Increased triglycerides are a risk factor for
cataract. Keeping blood levels of
triglycerides under control through diet
restrictions helps in preventing cataracts.
Diabetes greatly increases the risk of
developing a cataract. Diabetics should
check and control blood sugar levels
regularly.
Wearing sunglasses with UV- protection
when outside protects the eyes from
damage by the sun’s harmful UV rays.
Cataracts are a slow developing disease
which normally does not get detected
early. Regular eye exams by an eye
specialist can help in early detection of
the disease.