Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG) is a procedure performed to treat blocked or narrowed arteries that supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart. This is accomplished by going around or “bypassing” the blocked artery to increase the blood flow to the heart. CABG is used for people who have severe coronary heart disease (CHD), also called coronary artery disease (CAD).
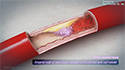
Coronary artery disease usually occurs when cholesterol and plaque accumulate inside the coronary arteries blocking the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscles. The plaque can sometimes break off and form a blood clot that can completely block the vessels, leading to permanent heart damage. CAD is the most common of all heart diseases, and a leading cause of death in both men and women.
Indications
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery is indicated for the treatment of narrowed and blocked coronary arteries, which can lead to serious complications if left untreated. The surgery may be performed on an emergency basis following a heart attack, or on an elective basis when conservative treatment measures have failed to relieve symptoms of coronary artery disease such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
Preparation for Surgery
Preoperative preparation for coronary artery bypass graft surgery may involve the following steps:
- A thorough history and physical examination
- Routine blood work and imaging
- Refraining from blood thinners, aspirin, or NSAIDs
- Informing your doctor of any allergies to medications, anesthesia, or latex
- Refraining from solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to surgery
- Arranging for someone to drive you home after surgery
- Signing a consent form after the risks and benefits of the surgery have been explained
Surgical procedure
Coronary artery bypass surgery is performed either through an open surgery or as a minimally invasive surgery. Traditionally, CABG is performed as an open-heart surgery and involves the following:
- You will lie on your back on the operating table.
- General anesthetic will be administered so you will be asleep and not feel any pain.
- Your surgeon will make an 8- to 10-inch-long incision down the middle of your chest bone (sternum).
- Special instruments called retractors are used to spread the ribs apart so the surgeon can access the heart.
- Your surgeon will inject a medicine or use electric shock to stop the heart beating. While your heart is stopped the blood will be redirected to a heart-lung bypass machine which functions similarly to your heart and lungs, supplying oxygen to the blood and keeping blood circulation moving.
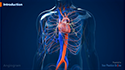
- Your doctor will harvest a piece of blood vessel (graft) usually taken from your leg (great saphenous vein) to construct a bypass by sewing one end of the harvested vein graft to a small opening made in the aorta (largest artery in the body), and the other end of the vein to an opening made in the coronary artery just below the blockage.
- After the bypass graft is established, blood flow through the heart-lung machine is disconnected and circulation will be restarted through the heart.
- Finally, the incision will be closed with absorbable sutures.
CABG surgery usually takes about 3 to 6 hours after which you will be transferred to the intensive care unit for monitoring.
Postoperative care
Common post-operative guidelines following coronary artery bypass graft surgery include the following:
- You will experience pain, soreness, and bruising around the incision site and graft sites for the first month or so. Medication will be provided as needed to keep you comfortable.
- Instructions on surgical site care and bathing restrictions will be provided.
- Your surgeon will give you activity restrictions such as no heavy lifting or strenuous exercise for the first few months to allow the sternum to heal completely.
- Your doctor will also prescribe blood-thinning medications to prevent blood clots and antibiotics to address the risk of surgery-related infection.
- You will be referred to a cardiac rehabilitation program to educate and assist you with your recovery. This usually involves exercise, lifestyle modification, and monitoring.
- A periodic follow-up appointment will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Risks and Complications
As with all surgical procedures, coronary artery bypass graft surgery may involve risks and complications including:
- Bleeding
- Heart rhythm irregularities
- Heart attack
- Stroke
- Infection of the wound
- Nerve and blood vessel damage
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Recurrent chest pain
- Adverse reactions to anesthesia
- Kidney or liver failure
- Scar formation
Summary
Coronary artery bypass grafting is a surgical procedure to bypass a blocked artery of the heart. It involves incising a small part of a blood vessel (most commonly a vein from the leg) and using it as a graft (piece of living tissue that is transplanted surgically). The procedure is indicated for the treatment of coronary artery disease, which is a serious risk factor for heart attack, and is very effective in reducing symptoms of angina, averting heart attacks, and reducing death.