Cardiac Ablation
Cardiac ablation is a procedure to treat heart rhythm problems referred to as cardiac arrhythmias. It involves the use of heat or cold energy to scar or destroy small areas of heart tissue, blocking the abnormal electrical signals that move through the heart and cause rhythmic disruptions.
Some of the types of heart rhythm problems include:
- Atrial fibrillation
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- Atrial flutter
- AV nodal re-entrant tachycardia (AVNRT)
- Accessory pathway, such as Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome
During cardiac ablation, small wires called electrodes are inserted within your heart through a blood vessel to evaluate your heart's electrical activity. When the root of the problem is discovered, the tissue causing the problem is ablated or destroyed.
Indications
When the heart beats, the electrical signals that prompt your heart to contract or squeeze should follow a specific pathway through the heart. Any disruption in the signaling pathway can cause an arrhythmia.
Your physician may recommend cardiac ablation for the correction of heart rhythm issues and to alleviate symptoms associated with it. Some of these symptoms include:
- Palpitations (a fluttering or skipping heartbeat)
- Chest pain
- Sweating
- Dizziness/lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Paleness
Your physician may recommend cardiac ablation if:
- Medications have failed to correct the heart rhythm problems
- You are experiencing severe side effects from medications
- You have increased risk of complications, such as sudden cardiac arrest due to arrythmias
- Other treatments such as cardioversion have failed to correct the abnormal heart rhythm.
- You have a specific type of arrhythmia such as supraventricular tachycardia or Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome that responds well to ablation.
Preparation for Cardiac Ablation
Preoperative preparation for a cardiac ablation procedure may involve the following:
- A review of your medical history and a thorough physical examination
- Routine blood work, imaging, and other tests specific to your condition
- Informing your doctor of any allergies to medications, anesthesia, or latex
- A review of your medications and the need to refrain from certain medications for a specific period
- Refraining from solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to the procedure
- Signing a consent form after the pros and cons of the procedure have been explained
Surgical procedure
Cardiac ablation can be performed by two methods.
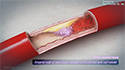
- Radiofrequency ablation: This method utilizes catheters to convey radiofrequency energy (similar to microwave heat) to destroy the problematic heart tissue.
- Cryoablation: This method utilizes a single catheter to deliver a balloon tipped with a freezing material to cause a scar in the problematic heart tissue.
Your physician will decide the best method suitable for you based on your heart rhythm problem.
In general, cardiac ablation involves the following steps:
- You will be administered a sedative drug just before the procedure to keep you relaxed.
- The skin on the groin, shoulder, or neck area is thoroughly cleaned and numbed with an anesthetic.
- A small incision is made in the area where the catheter (a small, flexible tube) is to be inserted.
- Next, a catheter is inserted through the incision into one of the blood vessels in the area.
- Your physician may inject a contrast medium (dye) through the catheter so that the blood vessels are clearly visible on X-ray images.
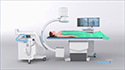
- Under live X-ray guidance, your physician carefully passes the catheter through the vessel up into your heart. Often, more than one catheter is required.
- Electrodes at the tip of the catheter are utilized to convey electrical signals and document your heart's electrical activity.
- Your physician utilizes this information to determine where to apply the ablation.
- Once the source of the problem has been identified, your physician will use electrical (or sometimes cold) energy to destroy the problem area in the heart, eliminating the heart rhythm problem.
Postoperative care
Cardiac ablation usually takes about 4 hours or more. After the procedure, you will be transferred to the recovery area where your vital signs are closely monitored. Based on your condition, you may be discharged home the same day or you may need an overnight stay in the hospital. Arrange for someone to drive you home after the procedure. You may experience some soreness at the incision site for a few days. Medications and use of a cold pack can help relieve the discomfort. Instructions on incision site care and bathing will be provided. You should avoid strenuous activities and lifting weights for a defined period. Most patients can resume their normal activities within a few days. A follow-up appointment will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Risks and Complications
Cardiac ablation is a relatively safe procedure; however, as with any procedure some risks and complications may occur such as:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Damage to heart valves
- Damage to blood vessels
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Slow heart rate
- Stroke
- Heart attack
- Death, in rare instances
Summary
Cardiac ablation, also known as catheter ablation or radiofrequency ablation, is a minimally invasive procedure that involves a small cut in the skin and the guiding of a tube into your heart through a blood vessel to eliminate small sections of heart tissue that may be triggering an abnormal heartbeat. The procedure helps to restore your normal heart rhythm and heart function and enables you to resume your active lifestyle without any functional limitations.