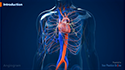
Atherosclerosis
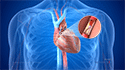
Atherosclerosis is a condition in which the arterial wall of the blood vessels is thickened and narrowed due to the deposition of fat or cholesterol forming a plaque. The rupture of plaque leads to formation of clots in the blood vessel. These plaques and clots can restrict blood flow to the organs; especially the heart. Atherosclerosis is the most common cause of cardiovascular diseases.
Causes.
The exact cause of atherosclerosis is not known, however it may start with damage to the inner layer of an artery. The damage to the arterial wall may be caused by various factors such as smoking, high levels of cholesterol in the blood, diabetes, and hypertension. Once the inner lining of the blood vessel is damaged, fatty deposits and other components of blood may begin to accumulate in the inner lining of the blood vessel. Over time, fatty deposits called plaque harden and narrow the arteries restricting the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your body.
Signs and symptoms.
Atherosclerosis usually causes no symptoms until an artery is severely narrowed or blocked or rupture occurs. Shortness of breath and pain in the chest and heart are the most common symptoms due to the interruption of blood flow through blood vessels. You may also feel numbness or weakness in arms and legs.
Diagnosis.
Your doctor will diagnose atherosclerosis based on your medical history, physical examination, and test results. Your doctor may recommend blood tests to measure the amount of cholesterol in the blood. Your doctor may use imaging studies such as ultrasound, and a computerized tomography (CT) scan to study your arteries.
Treatment of atherosclerosis:
The treatment options for atherosclerosis includes life style changes such as eating a healthy diet, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing stress. Your doctor may prescribe medications to lower your cholesterol level or blood pressure and help slow the progression of atherosclerosis. Your doctor may also prescribe antiplatelet medications to prevent the formation of blood clots. Surgical procedures involve widening of narrowed arteries (angioplasty) and redirecting the blood flow through other arteries (bypass grafting) in severe cases of atherosclerosis.
Prevention.
To prevent atherosclerosis and its related diseases it is recommended to control your risks factors as well as adopt a healthy life style.