Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
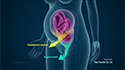
Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) is an endocrine disorder characterized by cysts in the ovaries, excessive androgen (male hormone) production by the ovaries, irregular menstruation and problems with the release of eggs (ovulation) for fertilization.
Causes.
The exact cause of PCOS is not known, but is most often associated with:
Genetics.
Insulin resistance.
Hormonal imbalance.
Signs and Symptoms.
The symptoms of polycystic ovarian syndrome vary from person to person and depend upon the nature and severity of the condition. Some of the symptoms of PCOS include:
Absent or irregular menstrual cycle.
Weight gain.
Abnormal patterns of facial and body hair.
Adult acne.
Hair loss or hair thinning from the head.
Difficulty conceiving.
Diagnosis.
Your doctor diagnoses PCOS on the basis of your medical history and by performing a thorough physical examination. Blood tests are ordered to determine the levels of various hormones, glucose tolerance and blood cholesterol.
A pelvic or vaginal ultrasound is performed to evaluate the appearance of the ovaries and the uterine lining.
Treatment.
Treatment is based on the symptoms and individual concerns. Treatment options include:
Lifestyle modifications include following a healthy balanced diet and regular exercise to keep your weight in check as obesity can worsen symptoms of PCOS.
Medications may be prescribed to treat different symptoms associated with PCOS, and may include:
Anti-diabetic medications.
Oral contraceptives may be prescribed for the management of irregular menstrual cycles. They reduce the level of male hormone, excessive body hair growth and the risks of uterine cancer.
Ovulation-inducing drugs or injection of gonadotropins (artificial hormones), namely follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) to treat fertility problems.
Oral medications and creams to slow down the growth of unwanted hair and prevent hair loss on the head.
Medication to reduce excess weight.
Surgery may be recommended in patients who do not respond to life style changes and medications.
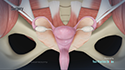
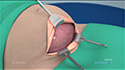
Laparoscopic ovarian drilling is an outpatient surgical procedure where a small incision is made in your abdomen and a thin needle with an electric current is inserted to destroy a section of the ovary. This helps to lower the levels of androgen production to facilitate regular ovulation.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is another treatment option where various techniques are performed to artificially fertilize and implant the egg for pregnancy. The process involves the induction of ovulation with medication, collection of matured eggs from the ovaries and combining them with the sperm in the laboratory. The eggs and sperm are left to fertilize in the lab and allowed to develop until the 5-day embryo stage. One or more mature
embryos are then removed and introduced into the uterus through the vagina. After transfer, if an embryo attaches or sticks to the womb lining, it results in pregnancy.
PCOS is a common endocrine disorder that has no cure. However, early diagnosis and treatment may help manage the disease and prevent other serious medical conditions such as diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular diseases, infertility, pregnancy-induced high blood pressure, anxiety and depression.